Rare Earth Filtration Solutions for Critical Mineral Processing
Why Are Rare Earth Elements Strategic for Clean Energy and Advanced Manufacturing?
Rare earth elements (REEs) underpin a wide range of advanced technologies, including electric mobility, renewable energy systems, electronics, and defense applications. Electric vehicles, wind turbines, and high-performance electronics all rely on rare earth materials to achieve efficiency, durability, and performance. As decarbonization targets accelerate, securing stable and resilient access to these materials has become both an industrial necessity and a geopolitical concern.
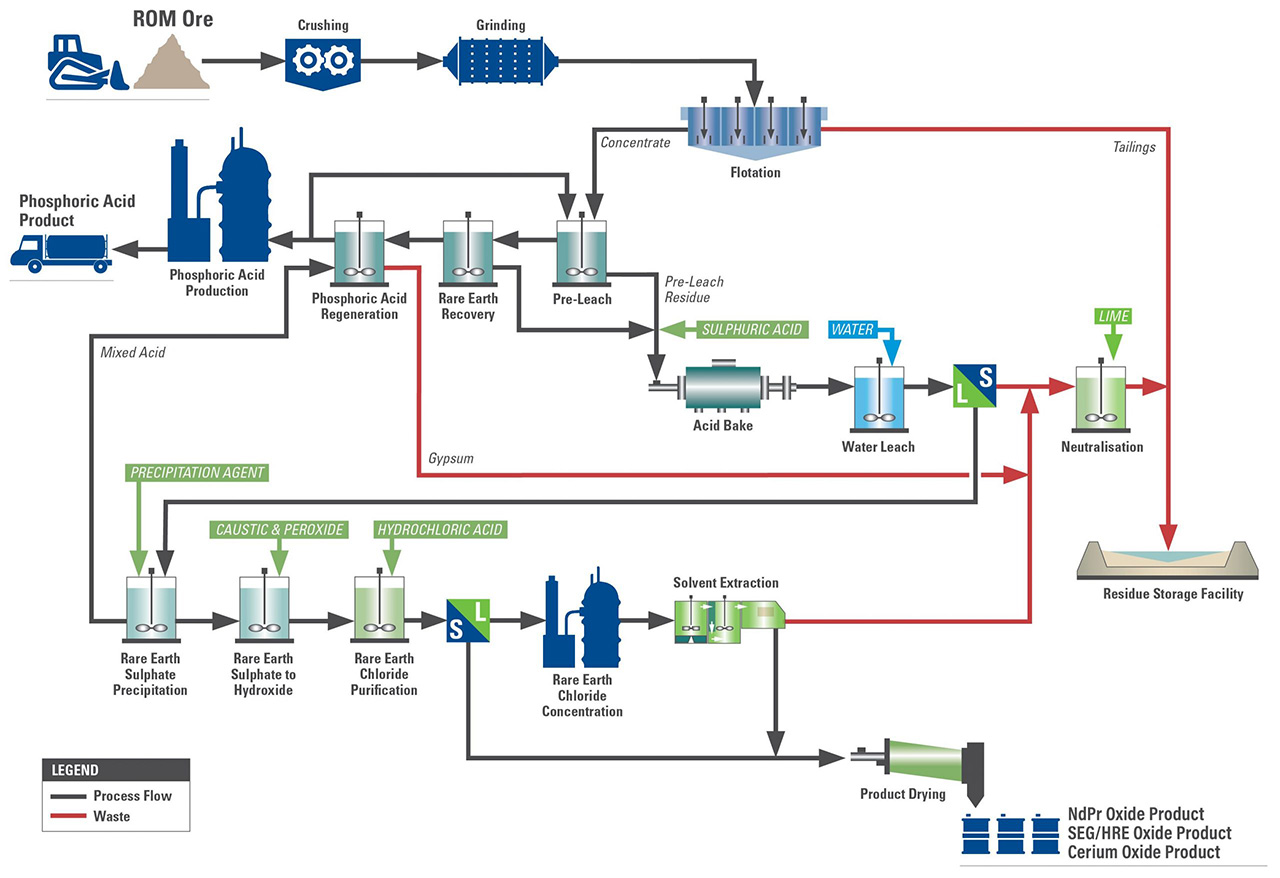
Although REEs are relatively abundant in the earth’s crust, their extraction and purification remain technically demanding. Rare earth deposits occur in different forms, including hard rock minerals such as bastnäsite and monazite, as well as ionic clay deposits. Each source requires distinct processing routes, often involving complex chemical treatment with acidic or caustic reagents. Across all flowsheets, reliable solid-liquid separation and recovery of valuable material is a decisive factor, making it a core unit operation in rare earth processing.
Why Is Solid-Liquid Separation Critical in Rare Earth Processing?
Rare earth processing typically requires multiple solid-liquid separation steps, which can vary significantly depending on the deposit type, chemistry, and overall process design.
Following mining, grinding, potential beneficiation and leaching, rare earth slurries contain dissolved REE species alongside a range of soluble and insoluble residues and fines.
In many complex rare earth flowsheets, these separation steps are found for leach residue removal, intermediate product recovery, and follow multiple precipitation stages for impurity removal from pregnant liquors. They are also located upstream of solvent extractions for clarification purposes as well as for final product isolation. Incomplete separation, product losses, or inconsistent filtration performance can directly impact product quality, chemical consumption, and overall process economics. Instabilities in solid-liquid separation can propagate through the entire process, affecting reagent efficiency, plant availability, and operating costs. As a result, filtration is increasingly viewed as a risk-critical operation rather than a secondary utility step.
Rather than representing a single unit operation, filtration technology must be adaptable across different chemistries, temperatures, and particle characteristics. Pressure candle filters are therefore often applied at several points within one processing plant.
What Technical Demands Do Rare Earth Filtration Applications Place on Equipment?
Rare earth filtration duties can involve radioactive materials, elevated slurry temperatures, fine particle sizes, and highly aggressive chemicals such as sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, oxalic acid, caustic soda, ammonium salts, and organic solvents. These conditions place significant demands on filtration equipment design and materials of construction.
Filters with a wide range of material options, minimal or no moving parts, and fully enclosed operation are therefore favored. Enclosed systems reduce operator exposure, while robust mechanical design improves reliability under demanding chemical and thermal conditions.
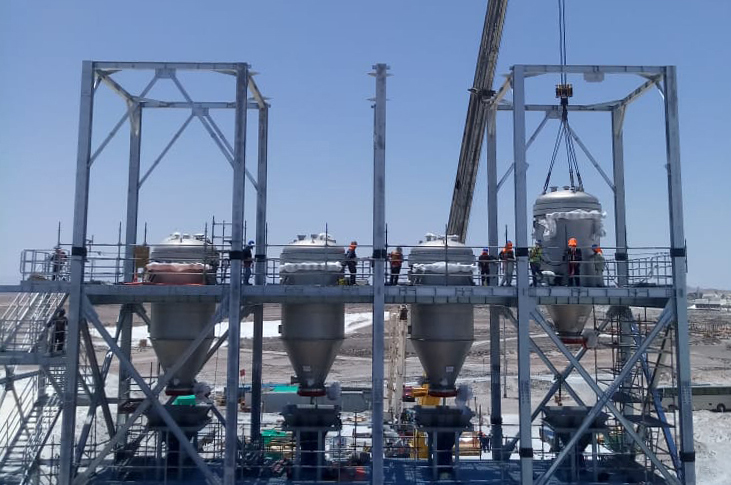
DrM’s FUNDABAC® candle filters are designed to meet these requirements. Engineered for aggressive environments and elevated temperatures, they provide automated, enclosed operation with consistent particle retention and effective cake washing. For rare earth processors, this supports stable recovery, improved operational safety, and reduced maintenance over the equipment lifecycle.
What Operational Challenges Do Rare Earth Processors Face in Filtration?
Rare earth processing places specific demands on solid-liquid separation equipment. Fine particle distributions, variable feed compositions, and aggressive slurries can lead to filtrate contamination, loss of valuable product, increased reagent consumption, and unplanned maintenance if filtration systems are not properly matched to the application.
Open or mechanically complex filtration technologies may also introduce safety and reliability concerns, particularly in corrosive or radioactive environments. As production volumes increase and purity specifications tighten, these challenges become more pronounced, reinforcing the need for robust, enclosed, and automated filtration solutions.
How Do Global Supply Chain Shifts Affect Rare Earth Processing Technologies?
With a significant share of global rare earth refining capacity historically concentrated in a limited number of regions, many economies are now accelerating investment in local processing and refining infrastructure.
As new projects move from feasibility into operation, attention is increasingly focused on process technologies that support reliable ramp-up and long-term stability. Solid-liquid separation plays a central role in this transition. FUNDABAC® filters are deployed in critical rare earth separation steps across Asia, North America, and Europe, supporting both greenfield developments and modernization projects. To date, more than 50 FUNDABAC® filters have been supplied specifically for rare earth applications, reflecting repeated selection for demanding process conditions.
When Is FUNDABAC® Filtration Typically Considered?
Pressure candle filtration is commonly selected in rare earth projects when radioactive materials are present, slurry temperatures are elevated, aggressive leaching chemistry is used, and fine solids must be retained with high efficiency. Consistent filtrate quality is often essential to protect downstream solvent extraction, precipitation, and final product quality.
FUNDABAC® systems are well suited where enclosed operation, automation, and low maintenance are critical to overall plant performance. These considerations apply both to new processing facilities and to retrofit projects seeking improved recovery, reliability, or safety without extensive changes to existing flowsheets.
Where Else Are Advanced Filtration Systems Used in Critical Minerals Processing?
DrM filtration systems are applied across a wide range of hydrometallurgical processes beyond rare earths. FUNDABAC® and CONTIBAC® filters support the production of lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide for battery applications, from both hard rock ores and brines, as well as high-purity manganese, cobalt, nickel, and graphite products.
In parallel, these systems contribute to more resource-efficient processing through applications such as brine recycling and closed-loop process concepts that reduce water consumption and improve overall plant efficiency.
How Does Filtration Support the Energy Transition?
Global demand for critical minerals is expected to increase significantly over the coming decades, placing pressure not only on extraction capacity but also on processing efficiency and reliability.
In this context, filtration is evolving from a supporting operation into a strategic lever for yield protection, process stability, and operational resilience. With more than 15 years of experience in rare earth solid-liquid separation and over 40 years of filtration expertise, DrM is well positioned to support the development, optimization, and troubleshooting of solid-liquid separation steps across rare earth and critical mineral processing flowsheets.